Ulysses HISCALE Data Analysis Handbook
Appendix 9 Geometric Factor Study for the Deflected and Unscattered Electrons of HISCALE (Buckley MS Thesis)
The model for the magnetic field in this study depends on the magnetization assigned to the two slabs of magnetic material located in the throat of the LEMS30 detector. As explained in Section A9.3, a linear falling model was selected for the magnetization, meaning that for each slab the magnetization is highest at the center of the magnets, and falls off linearly as one goes toward the edges:
M(x',y') = Mo + Ao |x'| + Bo|y'|
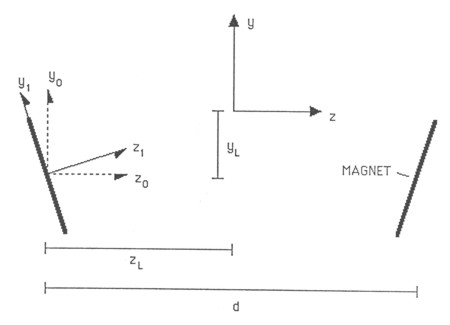
The parameters Ao, Bo, and Mo must all be chosen such that the model agrees with the calibration studies of J. W. Kohl. Other parameters that one must include are all listed in the file FDMOD1.CMN. In particular, parameters such as magnet length and width must be included, as well as the angle the magnets are tilted with respect to the y-axis of Shodhan's coordinate system. Also included in this file are translation parameters XL, YL, and ZL. These parameters translate the slabs from the (x',y',z') coordinates of the slab to the (x,y,z) coordinates of the deflection system, as shown below in Figure A9-21. The X0 and Y0 parameters are essentially "offset" values that allow one to control the location of maximum magnetization. Note that this .CMN file allows one to break the magnet up into any number of rectangular pieces, each assigned its own length, width, and translation parameters.
Figure A9-21 Definition of the translation parameters
Return to HISCALE List of Appendices
Return to Ulysses HISCALE Data Analysis Handbook Table of Contents
Updated 8/8/19, Cameron Crane
QUICK FACTS
Mission End Date: June 30, 2009
Destination: The inner heliosphere of the sun away from the ecliptic plane
Orbit: Elliptical orbit transversing the polar regions of the sun outside of the ecliptic plane



